The human brain is the command center for the human nervous system. It receives input from the sensory organs and sends output to the muscles. The human brain has the same basic structure as other mammal brains, but is larger in relation to body size than any other brains. Human nervous system is channeling the input signals through neurons in brain. Billions of neurons are connected in human brain and making a mesh which we called as neural network. The idea of this blog post is to show how we detect those neurons in human brain transmitting signals through brain. To capture the signals that are transmitting there is a way called as “Calcium image channeling”
What is Calcium Image Channeling?
In calcium image channeling, it sends calcium ions (Ca+2). Those Calcium ions play an integral role in neuron functioning. They act as intracellular signals that can elicit responses such as altered gene expression and neurotransmitter release from synaptic vesicles. Within the cell, calcium concentration is highly dynamic due to the presence of pumps that selectively transport these ions in response to a variety of signals. Calcium imaging takes advantage of intracellular calcium flux to directly visualize calcium signaling in living neurons. By using that intercellular calcium flux the images got in calcium image channeling will help to understand the path that signal is transmitting and using the path that we got it is easy to understand how brain functioning with neural network.
To use the calcium image channel in an efficient way there are lots of algorithms in use,
- Peeling algorithm
- Robust alignment method
- Motion correction algorithms
- Generalized transfer entropy
For calcium image channeling it is easy to use one of above algorithms. Let’s see about generalized transfer entropy
Generalized Transfer Entropy
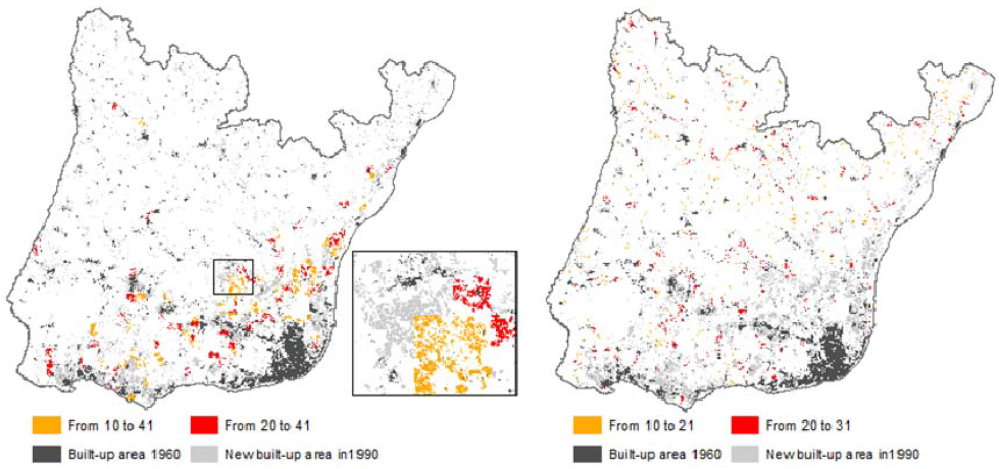
In modern chemical processes, identification of the process variable connectivity and their topology is vital for maintaining the operational safety. As a general information theoretic method, transfer entropy can analyze the causality between two variables based on estimation of conditional probability density functions. In calcium image channeling taking Ca+2 ions as one variable intracellular calcium flux which is changing as two variables we can easily get the outputs. But Transfer entropy estimation is typically a data driven method, however, the associated high computational complexity and poor accuracy are not acceptable in real applications. Using a nonlinear stochastic state-space model in conjunction with particle filters, a novel transfer entropy estimation method is proposed. The proposed approach requires less data, is fast and accurate.
Cross-correlation
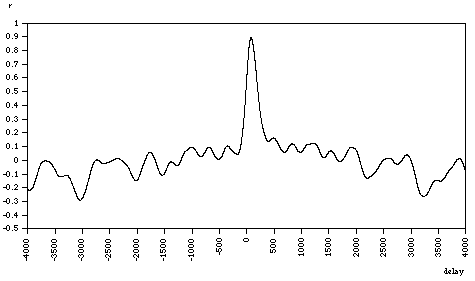
In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of two series as a function of the displacement of one relative to the other. In here we used one signal channel as Ca+2 ion intracellular calcium flux changing and other as when intracellular flux is not changing. Cross-correlation is also known as a sliding dot product or sliding inner-product. It is commonly used for searching a long signal for a shorter, known feature. It has applications in pattern recognition, single particle analysis, electron tomography, averaging, cryptanalysis, and neurophysiology.
In above two algorithms which we can used to increase the efficiency of calcium image channeling described. There are so many algorithms to increase the efficiency in this calcium image channel.